Fetching Datasource with Specific Item Data in Sitecore XM Cloud Using GraphQL
Published: 28 January 2026
Introduction
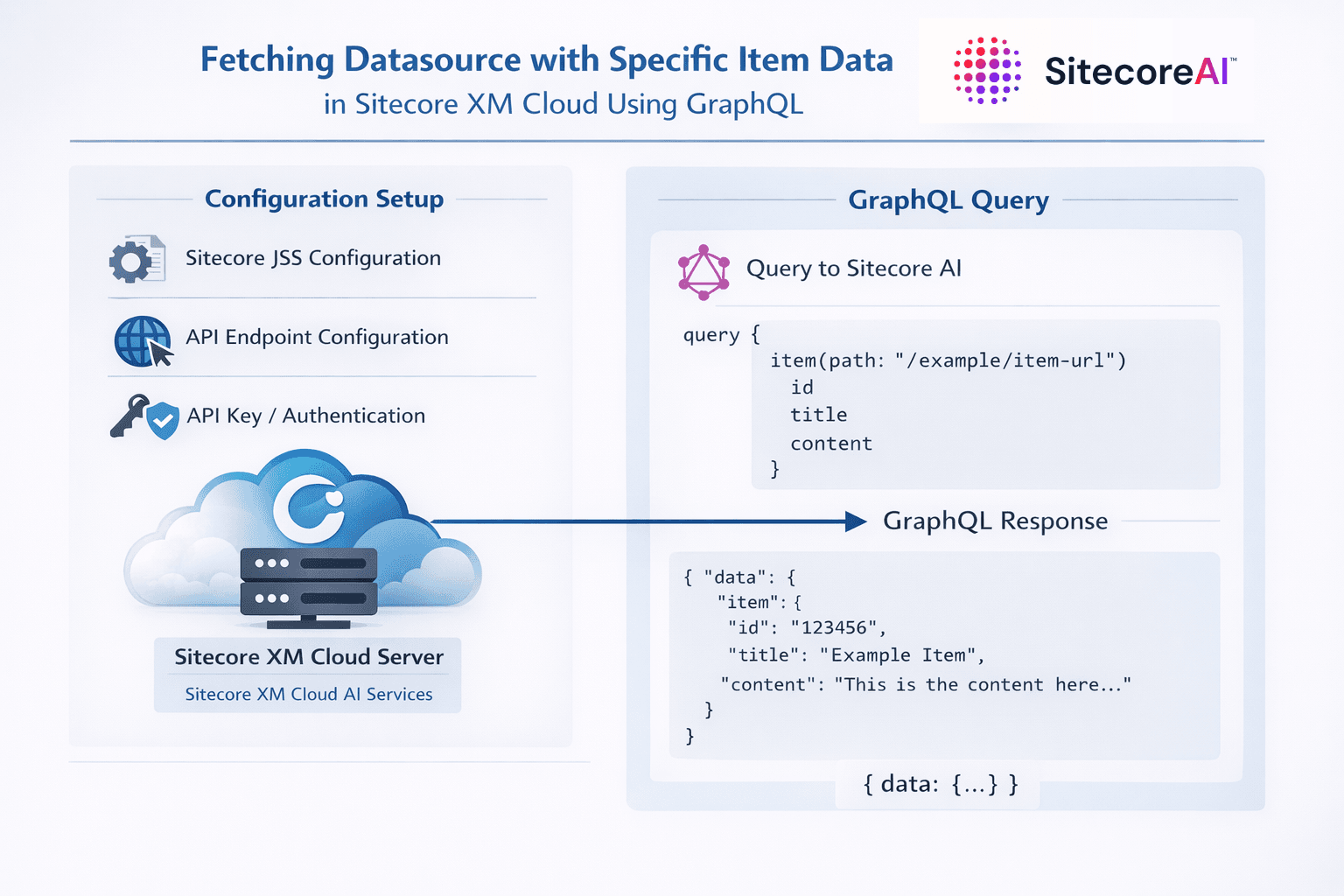
In Sitecore XM Cloud, GraphQL is the primary way to fetch structured content for headless applications. A common real-world requirement is to retrieve component-specific data from its datasource, while also querying related or global items in a single request. This blog explains how to achieve that using GraphQL, with a practical example that combines datasource-driven content and static site content.
This approach is especially useful for footer, header, or shared components where part of the data comes from the assigned datasource and part comes from a fixed content path.
Brief Overview of GraphQL in Sitecore XM Cloud
GraphQL in Sitecore XM Cloud allows frontend applications to request only the fields they need, reducing payload size and improving performance. Instead of multiple REST calls, a single GraphQL query can fetch data from multiple items, templates, and even languages.
XM Cloud provides GraphQL through:
- Preview GraphQL IDE (connected to the authoring environment)
- Experience Edge GraphQL IDE (connected to published content)
Both support advanced queries, variables, and field aliases.
Understanding Datasource-Based Queries
Each rendering in Sitecore XM Cloud can have a data source item assigned to it. When rendering a component, the front end may need:
- Fields from the data source item
- Additional content from other items (for example, navigation or footer links)
GraphQL makes it possible to fetch both in a single query by using variables.
Example GraphQL Query with Datasource and Static Item
Below is the GraphQL query used to fetch footer data from a Datasource and footer links from a fixed path:
query GetData ( $datasource: String!, $language: String! ) {
FooterData: item(path: $datasource, language: $language ) {
Logo: field(name: "Logo") {
jsonValue
}
Description: field(name: "Description") {
value
}
Address: field(name: "Address") {
value
}
}
FooterLinks: item(
path: “{Home-item-path}”,
language: $language
) {
Home: children(hasLayout: true) {
results {
displayName
__typename
ShowInFooter: field(name: "ShowInFooter") {
value
}
children(hasLayout: true) {
results {
displayName
ShowInFooter: field(name: "ShowInFooter") {
value
}
}
}
}
}
}
}Key Concepts Explained
1. Datasource as a Variable
The query uses a variable:
$datasource: String!
This is critical for reusable components where each instance(rendering) may point to a different item.
2. Field Aliasing
Aliases such as FooterData, FooterLinks, and Logo make the response more readable and frontend-friendly. This avoids naming conflicts and simplifies data consumption.
3. Mixing Dynamic and Static Content
- FooterData comes from the component’s datasource
- FooterLinks comes from a fixed content path
Both are returned in a single response, reducing API calls and improving performance.
Default Variables Commonly Used in Sitecore GraphQL
When working with XM Cloud and JSS-based applications, the following variables are commonly used:
datasource
Points to the datasource item assigned to the rendering.
contextItem
Refers to the current page item being rendered.
language
Specifies the content language (for example, "en"). This is critical for multi-language sites.
These variables are typically injected automatically by the rendering framework or passed explicitly from the frontend.
Where Sitecore AI Fits In
Sitecore AI complements GraphQL by helping teams:
- Analyse content performance
- Improve personalization and relevance
- Optimize structured content for reuse
When combined with GraphQL, AI-driven insights can help identify which fields are most valuable to expose, reduce over-fetching, and improve component design. While AI does not change the query syntax, it significantly improves how content is modeled and consumed.
Best Practices
- Always use variables for datasource and language to keep components reusable
- Use aliases to simplify frontend integration
- Avoid deeply nested queries unless required, as they can impact performance
- Test queries in Preview and Experience Edge separately
Conclusion
Fetching datasource-specific content along with related site content through GraphQL is a powerful pattern in Sitecore XM Cloud. By leveraging variables, aliases, and structured queries, developers can build highly reusable, performant components with clean data contracts.
This approach aligns well with XM Cloud’s headless architecture and scales effectively for enterprise implementations, making it a strong practice for modern Sitecore MVP-level solutions.
Vikesh Bhavsar
Associate Senior Software Engineer – Sitecore XM Cloud & SXA
Vikesh is a Sitecore professional at Addact with 4 years of experience, specializing in Sitecore XM Cloud, SXA, XP, and headless implementations, and delivering scalable, performance-driven CMS platforms.

